flowchart LR A["Input Layer (One Hot)"] A --> B["Embedding Layer"] B --> C["Sum/Average Layer"] C --> D["Output Layer"]
Embeddings
Revisiting what we know
Embeddings …
- transform text into numerical vectors
- are used in neural network architectures
- Key benefit: Capture semantic similarities and relationships between words
- Already seen: Bag of Words
- Issue: These embeddings do not compress!
What are embeddings?
- Represent words and text as dense, numerical vectors
- Capture rich semantic information
- Context-aware, based on surrounding text
- Capture subtle semantic relationships
- Compact representation compared to simple techniques such as bag of words
Approaches to generate embeddings:
- Word2Vec, GloVe, FastText
- Train neural network to predict surrounding words
- CBOW or skip-gram architectures
- Learns semantic relationships in continuous vector space
- Transformer architectures like GPT
- Word embeddings provided by OpenAI
What does it look like?
Train a model to:
- predict the target word based on the (surrounding) context words, or
- predict the context words given a target word
Use of the model
Throw away the parts after the embedding layer!
flowchart LR A["Input Layer (One Hot)"] A --> B["Embedding Layer"]
Matching with embeddings
Task: Find the matching document for a prompt
TrueGet the OpenAI client
Get the embeddings
Compute the similarity
import numpy as np
def cosine_similarity(vec1: np.array, vec2: np.array) -> float:
return np.dot(vec1, vec2) / ( np.linalg.norm(vec1) * np.linalg.norm(vec2) )
for text, text_embedding in zip(texts, text_embeddings):
similarity = cosine_similarity(text_embedding, prompt_embedding)
print(f"{text}: {round(similarity, 2)}")This is the first document.: 0.89
This document is the second document.: 0.65
And this is the third one.: 0.33Visualization and clustering
Define some words to visualize
Apply T-SNE to the embedding vectors
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
# Apply t-SNE dimensionality reduction
tsne = TSNE(
n_components=2,
random_state=42,
perplexity=5 # see documentation to set this correctly
)
embeddings_2d = tsne.fit_transform(np.array(embeddings))
# Plot the embeddings in a two-dimensional scatter plot
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 7))
for i, word in enumerate(words):
x, y = embeddings_2d[i]
plt.scatter(x, y, marker='o', color='red')
plt.text(x, y, word, fontsize=9)
plt.xlabel("t-SNE dimension 1")
plt.ylabel("t-SNE dimension 2")
plt.grid(True)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()Apply T-SNE to the embedding vectors
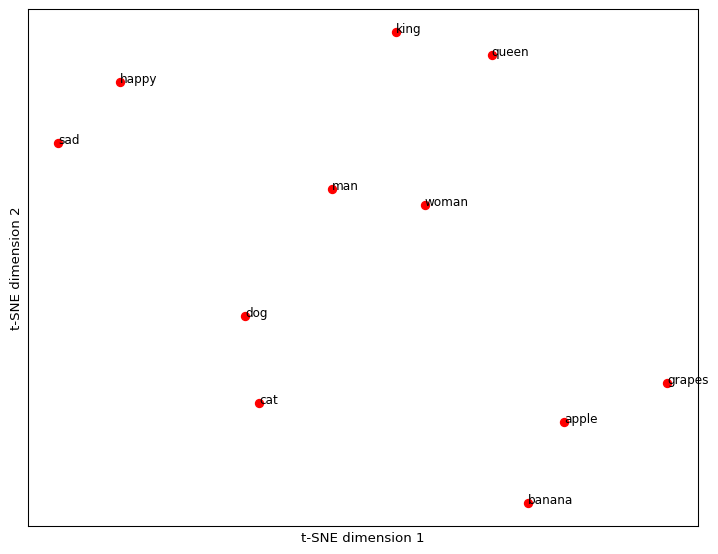
Cluster the embeddings
# do the clus#| tering
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
n_clusters = 5
# define the model
kmeans = KMeans(
n_clusters=n_clusters,
n_init="auto",
random_state=1 # do this to get the same output
)
# fit the model to the data
kmeans.fit(np.array(embeddings))
# get the cluster labels
cluster_labels = kmeans.labels_Visualize with T-SNE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
# Apply t-SNE dimensionality reduction
tsne = TSNE(
n_components=2,
random_state=42,
perplexity=5 # see documentation to set this correctly
)
embeddings_2d = tsne.fit_transform(np.array(embeddings))
# Define a color map for clusters
colors = plt.cm.viridis(np.linspace(0, 1, n_clusters))
# Plot the embeddings in a two-dimensional scatter plot
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 7))
for i, word in enumerate(words):
x, y = embeddings_2d[i]
cluster_label = cluster_labels[i]
color = colors[cluster_label]
plt.scatter(x, y, marker='o', color=color)
plt.text(x, y, word, fontsize=9)
plt.xlabel("t-SNE dimension 1")
plt.ylabel("t-SNE dimension 2")
plt.grid(True)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()Visualize with T-SNE
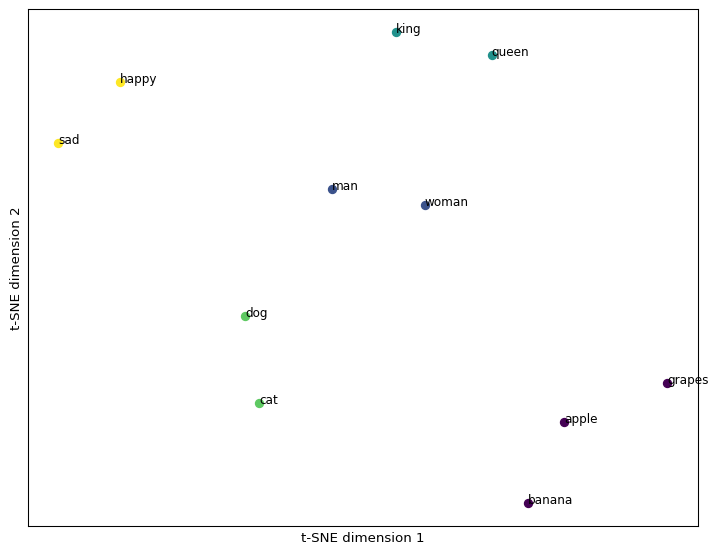
Seminar: LLM, SoSe 2025